Osteoarthritis: Navigating the Journey of Joint Health
Osteoarthritis is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide.
Let’s explore the key points about osteoarthritis in a clear and informative manner to help you understand and manage this condition better:
1. What is Osteoarthritis?
– Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that occurs when the protective cartilage that cushions the ends of bones wears down over time.
– It commonly affects weight-bearing joints such as knees, hips, and the spine, as well as hands and fingers.
2. Common Symptoms:
– Joint pain and stiffness, particularly after periods of inactivity or excessive use.
– Reduced joint flexibility and range of motion.
– Swelling and tenderness around affected joints.
– A grating sensation or bone-on-bone feeling during movement.
3. Risk Factors:
– Age: The risk of osteoarthritis increases with age.
– Obesity: Excess weight puts added stress on joints, contributing to cartilage breakdown.
– Joint Injuries: Previous joint injuries or overuse may lead to osteoarthritis in the affected joint.
– Genetics: Family history can play a role in predisposition to the condition.
4. Diagnosis:
– A medical evaluation and physical examination by a healthcare professional.
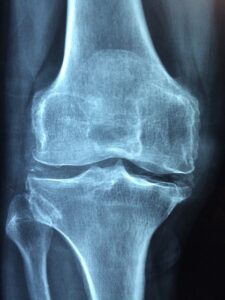
– Imaging tests like X-rays or MRIs to visualize joint damage and rule out other conditions.
5. Treatment and Management:
– Lifestyle Modifications:
– Maintain a healthy weight to reduce joint strain.
– Engage in regular low-impact exercise, such as swimming or walking.
– Protect joints during activities with proper techniques and joint-friendly equipment.
– Medications:
– Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
– Prescription medications for more severe pain and inflammation.
– Physical Therapy:
– Strengthening exercises to support joint stability.
– Range-of-motion exercises to improve flexibility.
– Assistive Devices:
– Use of braces or canes to provide joint support.
– Orthotics or shoe inserts to improve joint alignment and reduce pressure.
– Heat and Cold Therapy:
– Warm compresses to soothe stiff joints.
– Cold packs to reduce inflammation and swelling.
6. Coping with Osteoarthritis:
– Listen to your body and pace yourself during activities to avoid overexertion.
– Practice relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or meditation, to manage stress and pain.
– Seek emotional support from friends, family, or support groups.
7. Surgery:
– In severe cases, joint replacement surgery may be considered when other treatments no longer provide relief.